User guide for QuickPubMed
QuickPubMed provides easy access to perform complex searches in the PubMed database and includes both a simple and an advanced search function.
Here you can read more about the search function QuickPubMed and how to use it to easily find diabetes-relevant health science literature.
Note! You can get more information by hovering your mouse over the features in QuickPubMed or by clicking the  -icons.
-icons.
- Select a topic from the drop-down menu, or enter a search term if you cannot find a relevant one:

If the AI-assisted input feature is enabled, any search terms or questions you enter (in any language) will automatically be translated by artificial intelligence (AI) into a PubMed search. If you disable this feature, your search will be sent directly to PubMed exactly as you entered it. In that case, you need to use English words and search tags. Learn more about how to make PubMed searches, including the use of search tags.
- If necessary, combine multiple topics by:
Adding items in the same drop-down menu:

A combination of topics selected from different drop-down menus will retrieve articles that include at least one topic from each menu. For example: topic 1 AND topic 3.
... or select more topics:

A combination of multiple topics within the same drop-down menu will retrieve articles that include at least one of these topics, e.g. topic 1 OR topic 2.
or
Adding items to new drop-down menus:
Click the
 button and select one or more topics from the new dropdown menu.
button and select one or more topics from the new dropdown menu.A combination of items in multiple drop-down menus will find records that contain at least one item from each drop-down menu. E.g. type 2 diabetes AND carbohydrates.
- If necessary, select one or more limits to narrow your search:
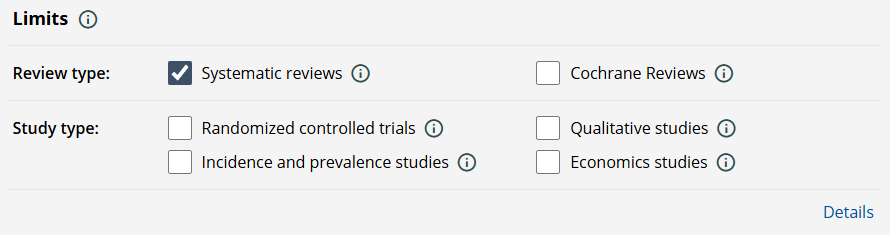
Note! To make your search as relevant as possible, additional filters that are not visible in this overview have already been applied. To view all the filters linked to your search, click 'Details'.
- Click the
 button
button
- When a search result is displayed, you will also find a number of features under each reference:
- Show abstract (button)
The abstract (summary) of the article to which the record refers is displayed. If there is no abstract, a button with the text 'Show info' is displayed. - Open in PubMed (button)
The reference is displayed in PubMed. PubMed opens in a new tab, so you can easily return to the tab with your current search in QuickPubMed. - Open journal (button)
The article is displayed on the journal's website. There you can read more about the article, and find out if you can read it for free or buy access to the entire jpurnal article. - Altmetric (icon)
Displays a score that reflects how often that article has been featured in various media such as social media, news media, and guidelines. The different colors indicate which media have covered the article. Read more about Altmetric. - Dimensions (icon)
Indicates how many times the article has been cited in other scientific articles. Read more about Dimensions.
- Show abstract (button)
- When you click on the 'Show abstract' button, you will find additional feature under the abstract:
- Summarize the abstract with AI (open/close)
Using artificial intelligence (AI), the abstract can be summarized in either plain language or technical language.Click one of the two buttons to start the summarization. In some cases, while the summary is being generated, you may also see the full-text article summarized in a structured format, and you will be able to ask questions and receive answers based on the article’s content.
This happens automatically if free access is available to the full-text article, and it is published under one of the following open-access license types: CC BY, CC BY-SA, CC BY-NC, CC BY-NC-SA, or CC0, all of which permit the text to be transformed into new content. - Download PDF / Read full-text article / Find PDF on journal website (icon + link)
Indicates whether you can access the full article. Depending on what is available, you will see one of the following links:- Download PDF: Go directly to or download a free PDF version of the article.
- Read full article: The article is not available as a PDF, but you can read it for free as web text.
- Find PDF on journal website: The article is not freely available, but you can visit the journal’s website page where you may be able to purchase access to the article.
- Similar articles in PubMed (link)
Displays a list of PubMed records that are similar to the one you have clicked. The list is based on PubMed's search algorithms for similarity. - Similar systematic reviews in PubMed (link)
Corresponds to the 'Similar articles in PubMed' feature above, with the difference that this list is limited to records categorized as systematic reviews. - Articles frequently viewed together with this in PubMed (link)
Displays a list in PubMed of records that others have also clicked on while clicking on that record in PubMed. - Download PDF of full text article (if available) (link)
Go directly to the PDF version of the article, if available. Some articles are available for free in PDF format, while you have to pay to access others. If the article is not available for free, you will simply be forwarded to the journal's website when you click on this link. If you find that nothing happened when you click on the link, copy the link and paste it into a new tab. - Search for this article on Google Scholar (link)
Searches for the reference to the current article in Google Scholar, where you can make use of various features such as seeing who cited the article, finding different versions of it and related articles.
- Summarize the abstract with AI (open/close)
- When you click 'Search', the following two features will appear just above the list of search results:
- Generate AI summary of search result (open/close)
Select the articles in the search results whose abstracts you want to have summarized by marking them. If you do not select any, the abstracts from the first five articles will be summarized. The summaries are generated using artificial intelligence (AI) and can be displayed either in plain language or in professional language. Click one of the two buttons to start the summarization. - Selected record (open/close)
An overview of the articles you have selected. Selected articles can be summarized using artificial intelligence (AI) or shared with others. You can share your selected articles together with the current search by clicking the 'Copy link' button.
- Generate AI summary of search result (open/close)
Click on the 'Advanced search' tab and follow the same steps as for 'Simple search'.
The differences from simple search are that in advanced search you can:
- Choose between searches with different scopes:
- Narrow: Search with high specificity, i.e. the vast majority of records in the search result are relevant, but at the same time you must expect that some relevant records will not be found.
- Standard: Search with a good balance between specificity and sensitivity, i.e. the search result contains many relevant records but also a few irrelevant ones.
- Broad: Search with high sensitivity, i.e. that there are several relevant, but also some irrelevant, records.
- Add more limits
In the first drop-down menu under 'Filters', you can choose from a range of categories. When you select a category, a new drop-down menu will appear, allowing you to add one or more filters.
Once you have selected a topic, you can access a number of features by clicking the 'Details' link:
- Your search
Displays a readable version of your search. This means that the combination of the choices you have made in the search form is described in "natural language". - Show search string
Displays your search as it would look if you were to perform the same search directly in PubMed with a so-called search string. By clicking the box once, you copy the search string. - Run search in PubMed
Submits your search to PubMed so you can see your search results there. - Create alert in PubMed
Receive an email when the search you have build in the search form returns new results. NOTE! Only works if you are already logged in to PubMed in the same browser when you click on the link. If you do not already have an account, create an NCBI account. - Reset
Removes all the choices you made in the form. All default selections under 'Limits' are set as when you started. - Copy link
The link to the search currently displayed on the search form is copied. Can be used to save under 'Favorites' in your browser or to share a specific search with others.